Amazon QLDB - Overview
- QLDB = Quantum Ledger Database
- Fully managed, serverless ledger database
- Has built-in, immutable journal to record all the change history of your data
- Transparent and cryptographically verifiable ledger
- Tracks each application data change and maintains a complete and verifiable history of changes over time.
- Supports ACID transactions
- Uses query lanague named PartiQL (SQL-like, Open standard)
- Uses Amazon ION format
- A Superset of JSON
- Self-describing, hierarchical data serialization format
- Offers interchangeable binary and text representations
- Adds additional data types, type annotations and comments to JSON format
- Supports nested JSON elements
- Use cases: System of record applications like Banking transactions, HR services records, Insurance claim histories, Vehicle ownership records etc.
QLDB Architecture
- It's serverless (scales automatically to support the needs of your application)
- Intended to support high-performance OLTP workloads


- Ledger = Journal + set of tables
- Journal
- Is append-only, immutable
- No updates / overwrites / deletes
- Stores a sequenced, cryptographically verifiable entry of each change to the table data
- Changes are chained together as blocks (but not a blockchain implementation)
- QLDB is centralized and not a distributed ledger (blockchain is used with decentralized use-cases)
- Even if you delete data from the ledger(table), you can access its change history from the immutable journal
- Tables
- Collection of documents and their revisions
- Store the current and historical state of your data (indexed storage)
- Can include document deletion records
- Documents are in ION format
Relational vs Ledger
| Rleational | Ledger(QLDB) |
| Database | Ledger |
| Table | Table |
| Index | Index |
| Table row | Document |
| Column | Documnet attribute |
| SQL | PartiQL |
| Audit Logs | Journal |
QLDB Views

- QLDB offers three views of your data
- User view
- Committed view
- History view
- User view
- latest version of your data
- default view
- Committed view
- user view + system generated metadata
- History view
- contains all historical document revisions
- i.e. all change history with metadata
Working with QLDB
- You create a ledger and define your tables
- QLDB supports ACID semantics
- We use PartiQL query language to query QLDB
- It's a SQL-like open standard query language
- SQL-compatible access to relational, semi-structured, and nested data
- Extends SQL to support ION documents
- PartiQL is also used with Redshift / S3 select / Glacier Select
Amazon ION format

- Is a Superset of JSON
- Self-describing, hierarchical data serialization format (=nested JSON)
- Offers interchangeable binary and text representations
- Adds additional data types, type annotations and comments to JSON format
- Flexible data model
Data Verification in QLDB

- Journal maintains immutable and verifiable transaction log
- QLDB uses a digest for verification
- Digest
- is a cryptographic representation of your journal
- or a unique signature of your data's entire change history as of a point in time
- is generated using SHA-256 hash function with a Merkle tree-based model
- Can verify the integrity of your data by calculating the digest and comparing it with QLDB's digest
- Can verify using the AWS console or QLDB API
- Improper verification requests typically result in IllegalArgumentException
Demo
QLDB Backup and Restore

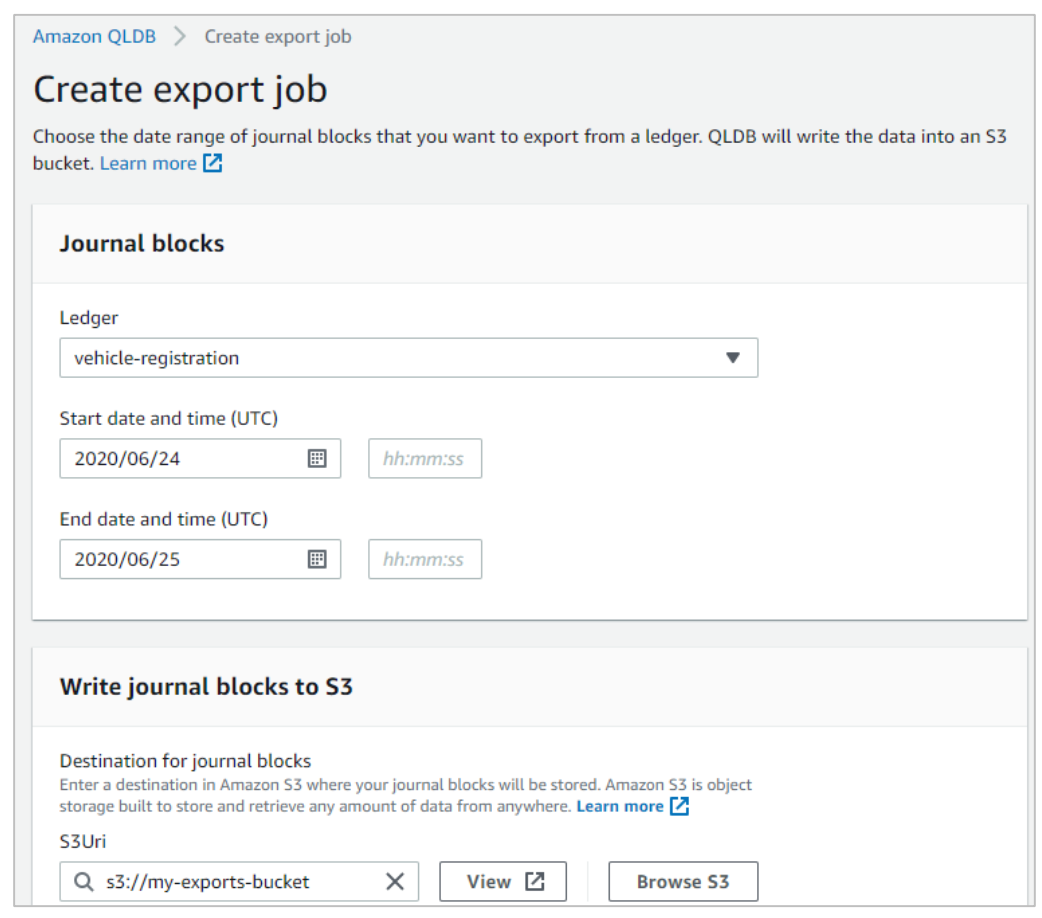
- QLDB does not support a backup and restore feature (yet!)
- PITR is. also not supported (yet!)
- Can only export your QLDB journal to S3
- For analytics / auditing /data retention / verification / exporting to other systems
- limit of two concurrent journal export jobs
QLDB Streams
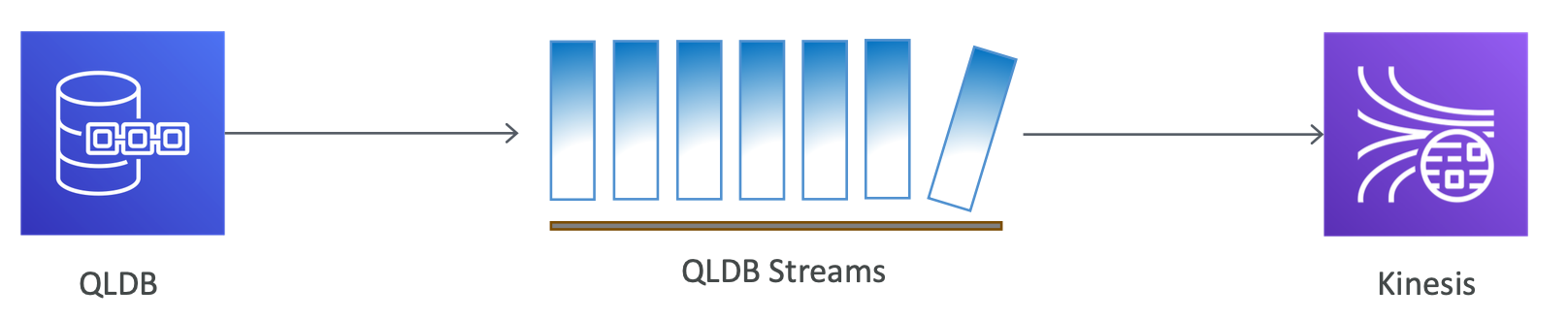
- Continuous flow of data from your ledger's journal to a Kinesisi data stream
- Provides an at-least-once delivery guarantee
- No ordering guarantees
- Revisions can be produced in a Kinesis data stream out of order
QLDB High Availability and D urability
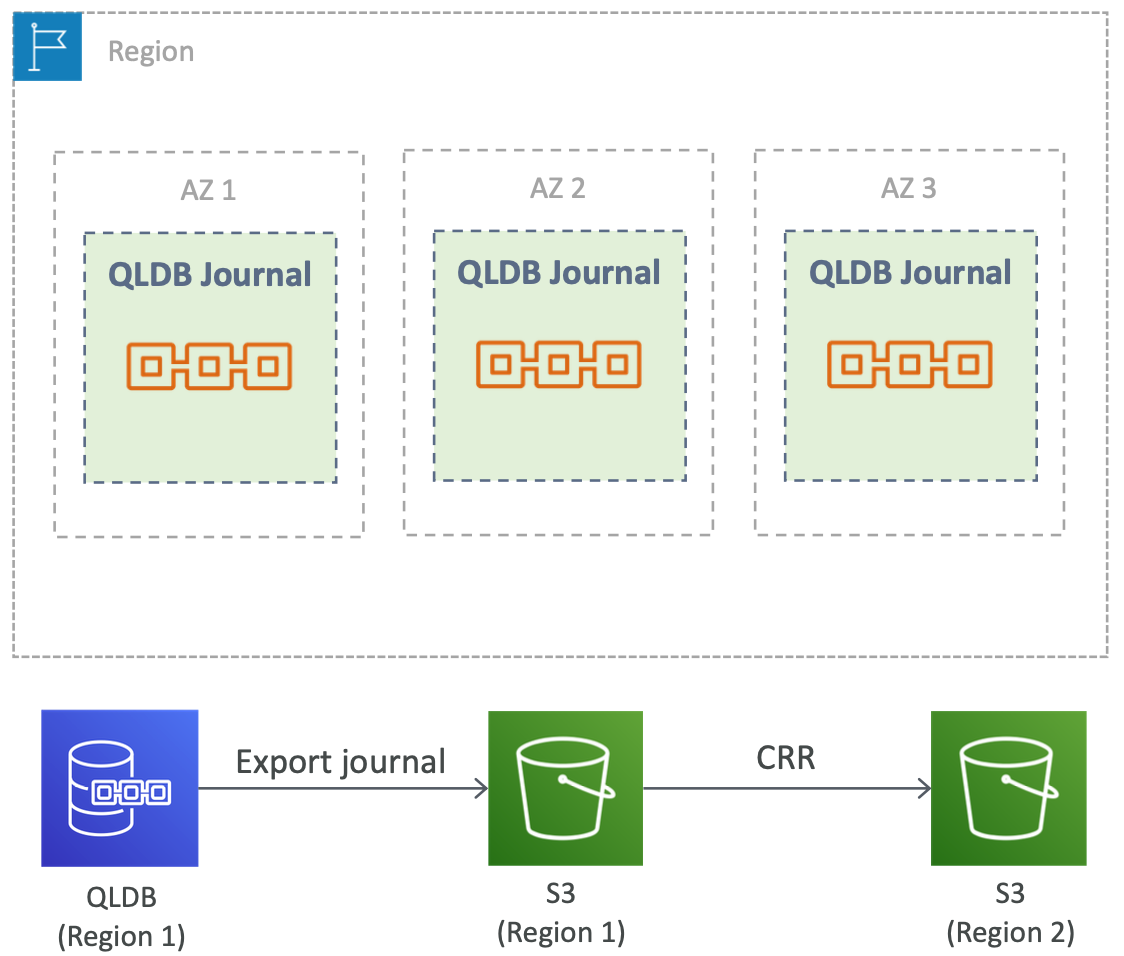
- QLDB ledger is replicated across multiple AZs within the region (=high availability)
- With multiple copies per AZ (=strong durability)
- Write is acknowledged only after being written to a durable storage in multiple AZs
- CRR is not supproted (yet!)
- QLDB journal can be exported to an S3 bucket
- S3 bucket cna then be configured for CRR
QLDB Security
- IAM is used for authentication and authroization of QLDB resources
- Supports encryption at rest and in transit
- Uses Amazon-owned keys to encrypt QLDB data
- Does not support CMKs
QLDB Security - Networking
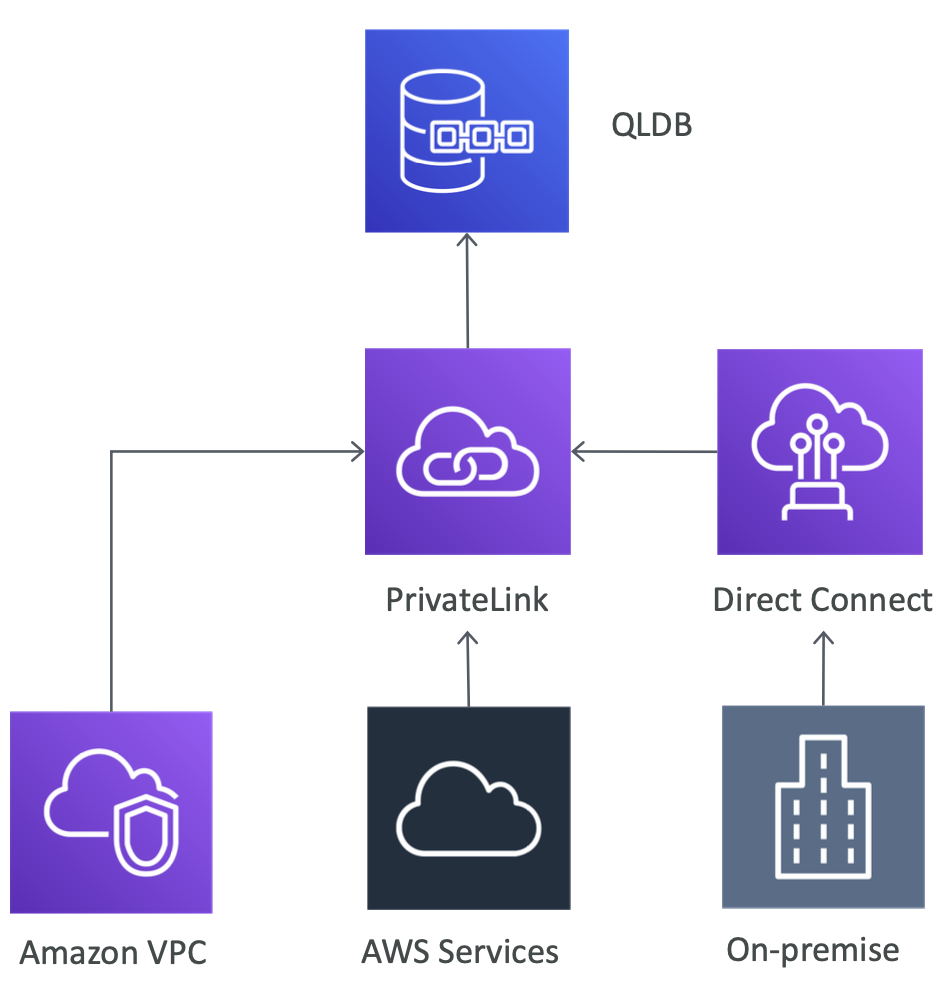
- Can use an interface VPC endpoint to allow VPC resources to connect to QLDB privately
- Interface VPC endpoints are powered by AWS PrivateLink
- PrivateLink provides private and secured connectivity between VPCs, AWS services, and on-premises applications
- PrivateLink eliminates the need for IG / NAT device / VPN connection / or AWS Direct Connect connection
QLDB Monitoring
- Integrated with CloudWatch (Alarms / Logs / Events)
- Comon metrics
- JournalStorage
- IndexedStorage
- ReadIOs
- WriteIOs
- CommandLatency
- QLDB log files provide additional information
- API calls and user activity can be logged with CloudTrail
QLDB Pricing
- You pay only for what you use
- Storage - per GB per month
- Journal Storage and Indexed Storage
- IOs - per million requests
- read IOs and write IOs
- Data transfer
'AWS Database > AWS Other Database' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Keyspaces (Cassandra) (0) | 2022.01.20 |
|---|---|
| [AWS Certificate]-Amazon Timestream (0) | 2022.01.16 |
| [AWS Certificate]-Amazon Elasticsearch Service (0) | 2022.01.16 |
| [AWS Certificate]-Amazon Neptune (0) | 2022.01.16 |
| [AWS Certificate]-DocumentDB (0) | 2022.01.15 |



