Multi-AZ Deployments in RDS

- For high availability, data durability and fault-tolerance (not used for scaling)
- Offers SYNC replication to standby instance in another AZ over low latency links
- Performs automatic failover to standby instance in another AZ in case of planned or unplanned outage
- Uses DNS routing to point to the new master (no need to update connection strings)
- Failover time (RTO) are typically 60-120 seconds (minimal downtime)
- Backups are taken from standby instead of primary to ensure performance level during backup activity
- Recommended for production use cases
- To force a failover or simulate AZ-failure, reboot the master instance and choose Reboot with failover
RDS Read Replicas

- Read-only copies of master(primary) DB instance
- Up to 5 Read Replicas
- Within AZ, Cross AZ or Cross Region
- Replication is ASYNC, so reads are eventually consistent
- Applications must update the connection string to leverage read replicas
RDS Read Replicas

- Boost DB performance and durability
- Useful for scaling of read-heavy workloads
- Can be promoted to primary (complements Multi-AZ)
- To create a replica, you must enable automatic backups with at least one day retention period
- Replica can be Multi-AZ (= a replica with its own standby instance)
Multi-AZ Replicas in RDS

RDS Read Replicas as Multi-AZ

- Supported for MySQL / MariaDB / PostgreSQL / Oracle
- Works as a DR target. When promoted to primary, it works as Multi-AZ
- There's added network cost when data goes from one AZ to another
RDS Read Replicas - Use Case

- You have a production database that is taking on normal load
- You want to run a reporting application to run some analytics
- You create a Read Replica to run the new workload there
- The production application is unaffected
- Read replicas are used for SELECT (=read) only kind of statements (not INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE)
Promoting a Read Replica to a Standalone DB Instance

- Promoted instance is rebooted and becomes an independent DB instance (separate from its source)
- Will no longer work as a replica. Does not affect other replicas of the original DB instance
- You cannot promote a replica to standalone instance while a backup is running
Promoting a Read Replica to a Standalone DB Instance - Use cases
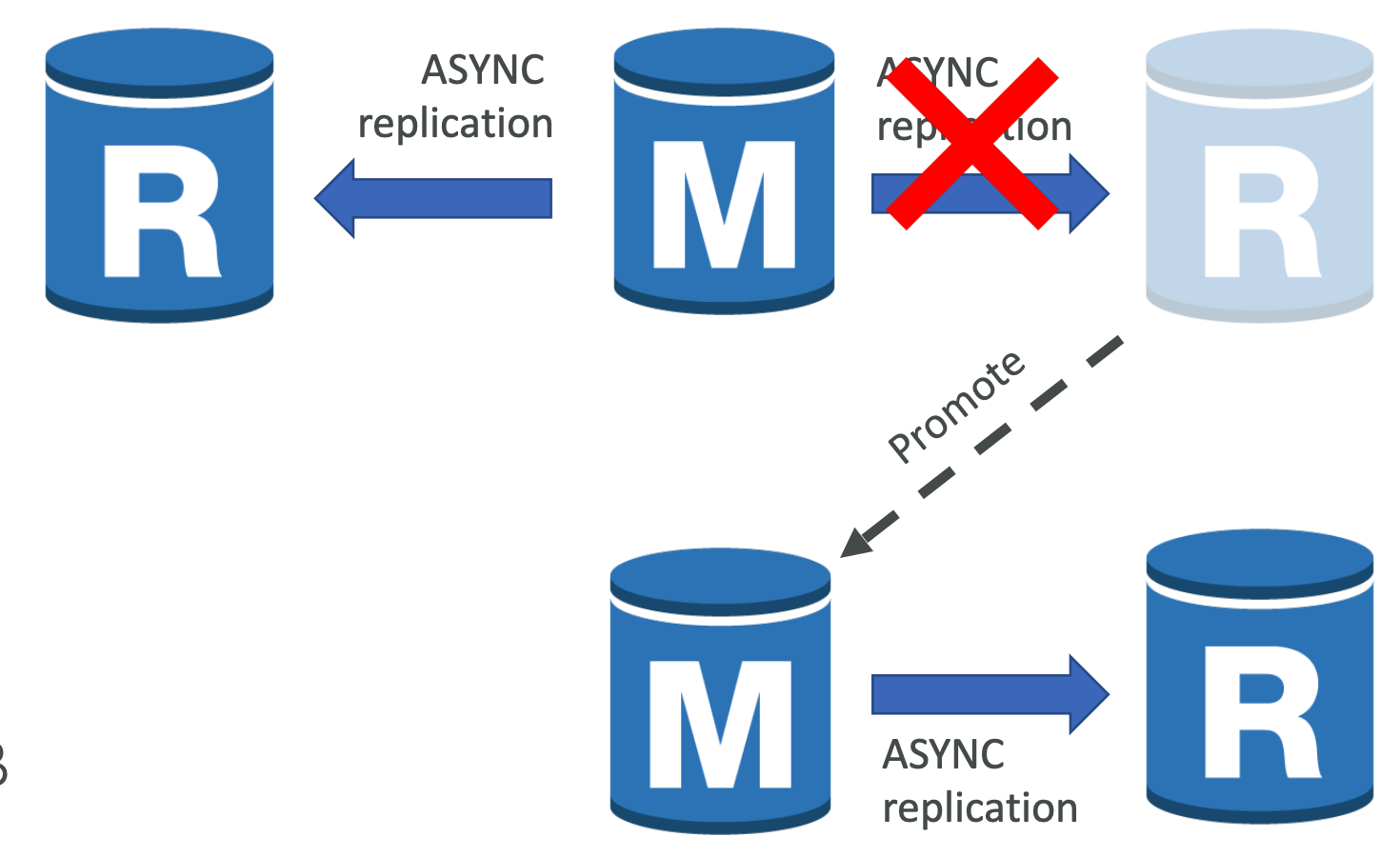
- Use as a DR strategy
- Avoid performance penalty of DDL operations (like rebuilding indexes)
- perform DDL ops on a read replica and promote it to a standalone instance. Then point your app to this new instance.
- Sharding (splitting a large DB into multiple smaller DBs)
--- Demo ---
Enabling writes on a read replica
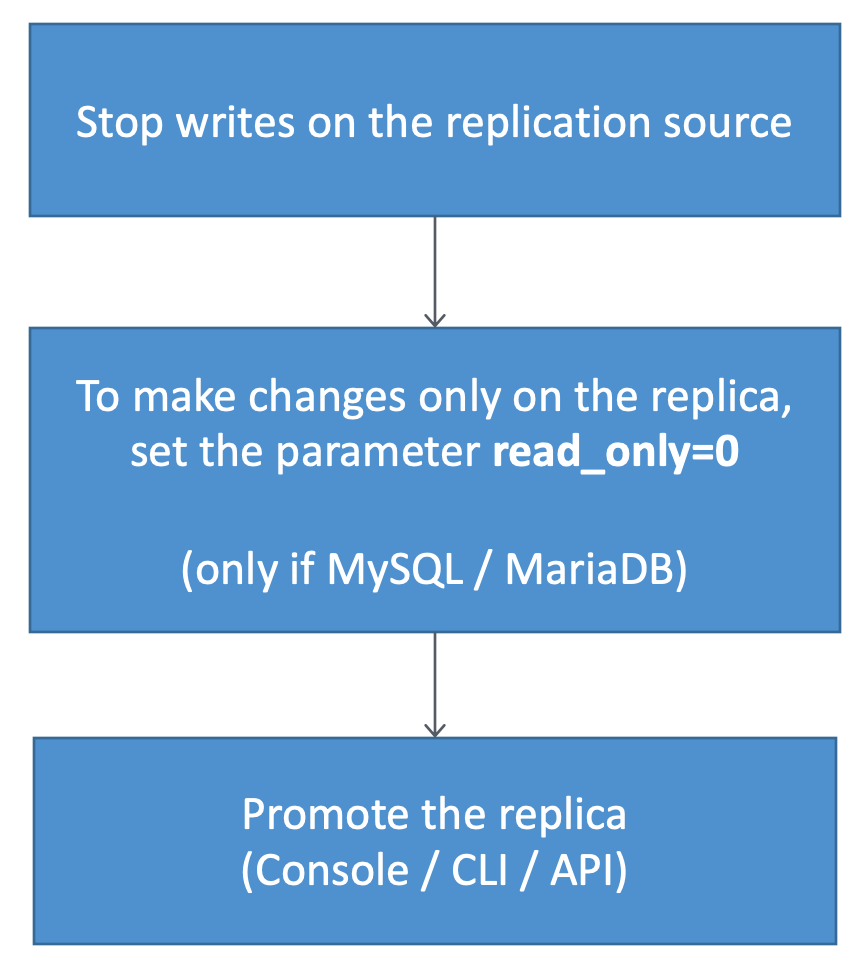
- For MySQL / MariaDB read replica, set the parameter read_only = 0 for the read replica to make it writable
- You can then perform DDL operations on the read replica as needed without affecting the source DB
- Actions taken on the read replica don't affect the performance of the source DB instance
- You can then promote the replica to a standalone DB
RDS Read Replica Capabilities
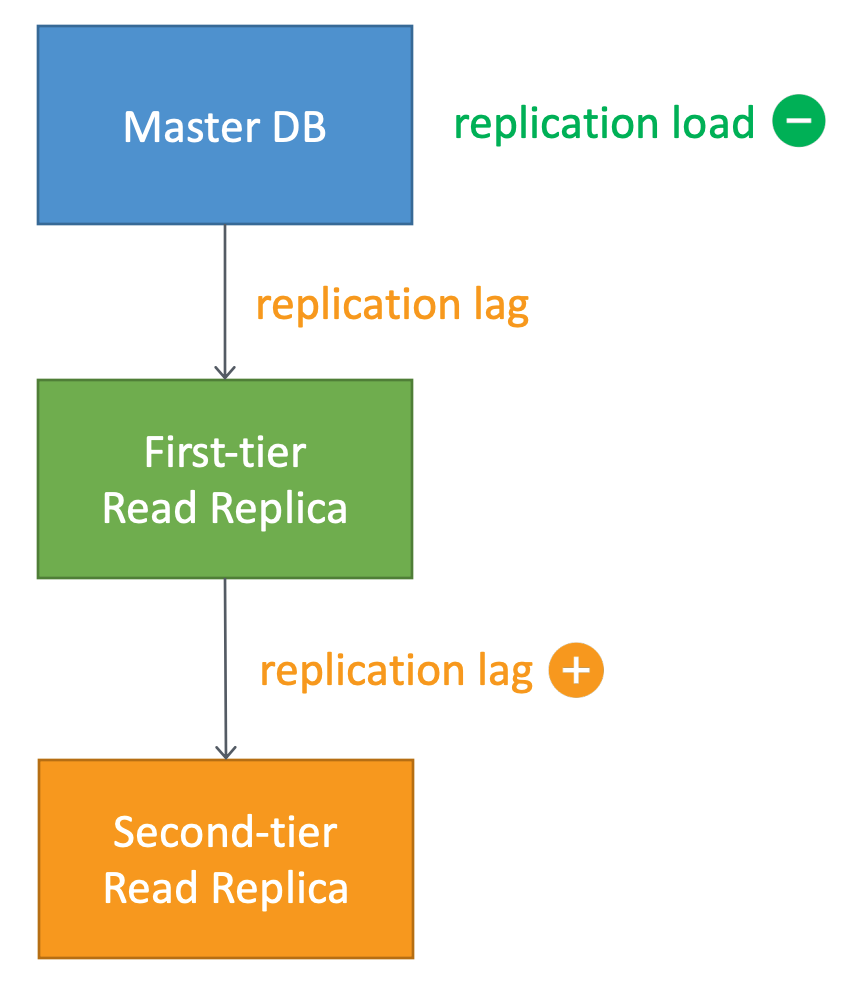
- Can create multiple read replicas in q uick succession
- Can use DB snapshot to perform PITR of a Read Replica
- Can create a replica from an existing replica
- reduces replication load from the master DB instance
- second-tier replica can have higher replication lag
Demo
Cross-Region Read Replicas in RDS
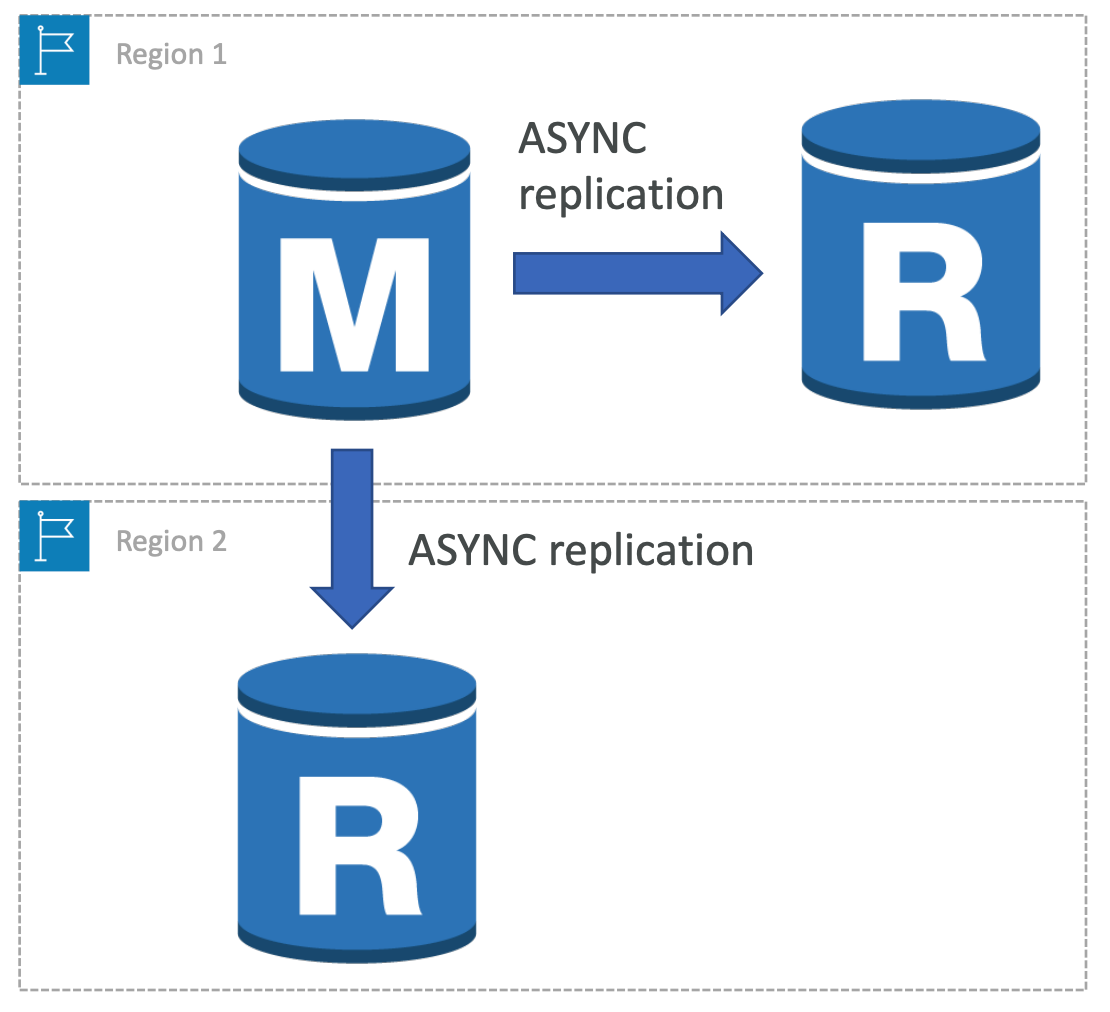
- Supported for MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL
- Not supported for SQL Server
- Advantages
- Enahanced DR capability
- Scale read operations closer to the end-users
- Limitations
- Higher replica lag times
- AWS does not guarantee more than five cross-region read replica instances
RDS replicas with an external database
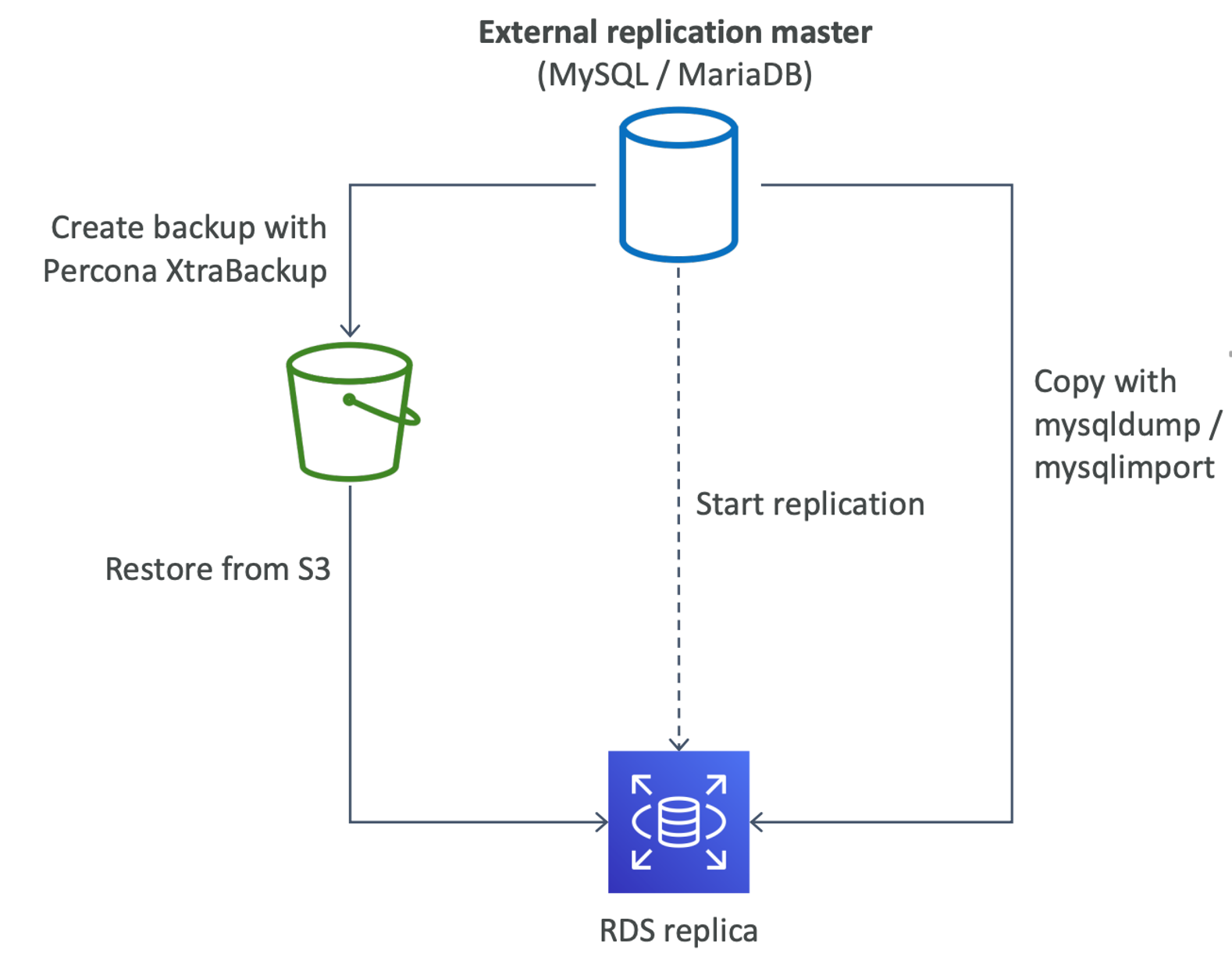
- Replication b/w an external DB and an RDS replica
- Supported for MySQL / MariaDB engines
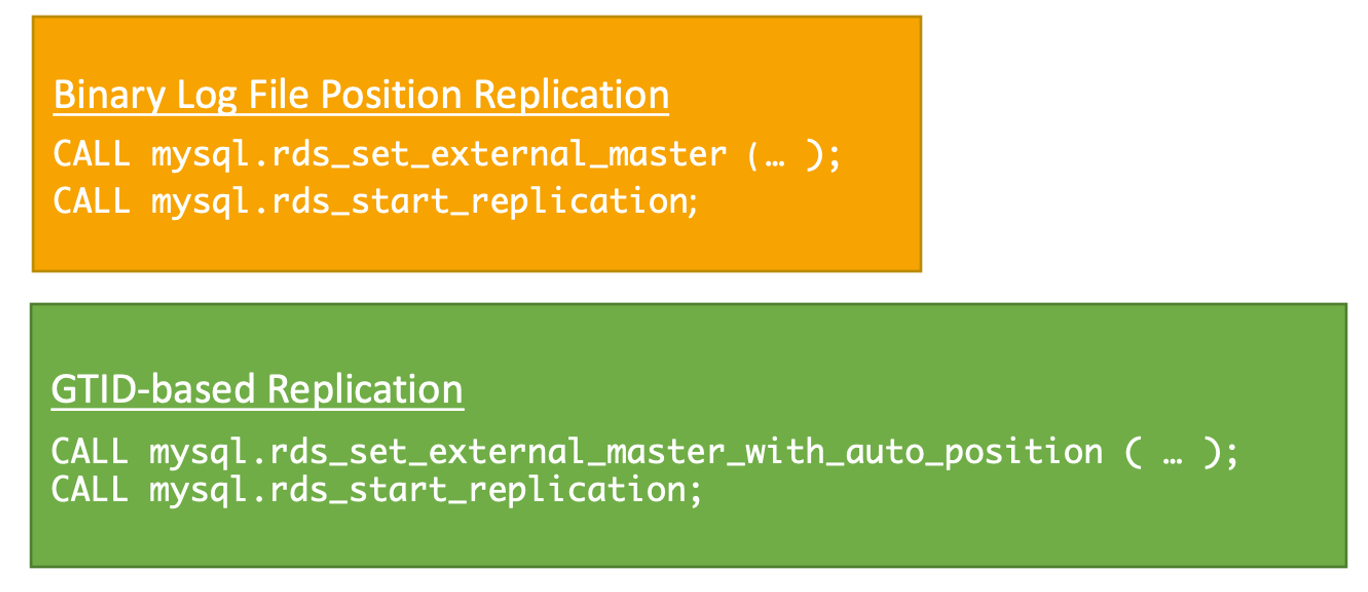
- Two ways
- Binlog replication
- GTID based Replication
RDS Disaster Recovery Strategies
- To ensure business continuity despite unexpected failures/events
- Multi-AZ is not enough (it can't protect from logical DB corruption, malicious attacks etc.)
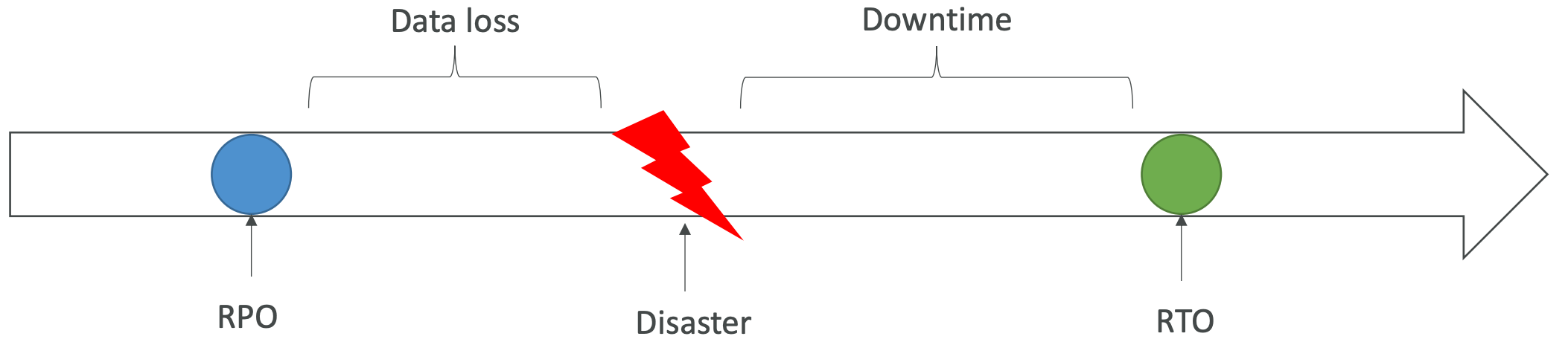
- Key metrics for DR plan - RTO and RPO
- RDS PITR offers RPO of 5 minutes (typically)
- RTO (Recovery time objective)
- How long it takes you to recover after a disaster
- Expressed in hours
- RPO (Recovery point objective)
- How much data you could lose due to a disaster
- Expressed in hours (e.g. RPO of 1 hour means you could lose an hour worth of data)
Comparing RDS DR Strategies
| RTO | RPO | Cost | Scope | |
| Automated backups | Good | Better | Low | Single Region |
| Manual snapshots | Better | Good | Medium | Cross-Region |
| Read replicas | Best | Best | High | Cross-Region |
- Replica lag - the amount of time that the replica is behind the source DB
- Replica lag can impact your recovery
- Failover to an RDS read replica is a manual process (not automated)
- A good DR plan should include a combination of backups, replicas and Multi-AZ/Multi-region deployment
Troubleshooting high replica lag
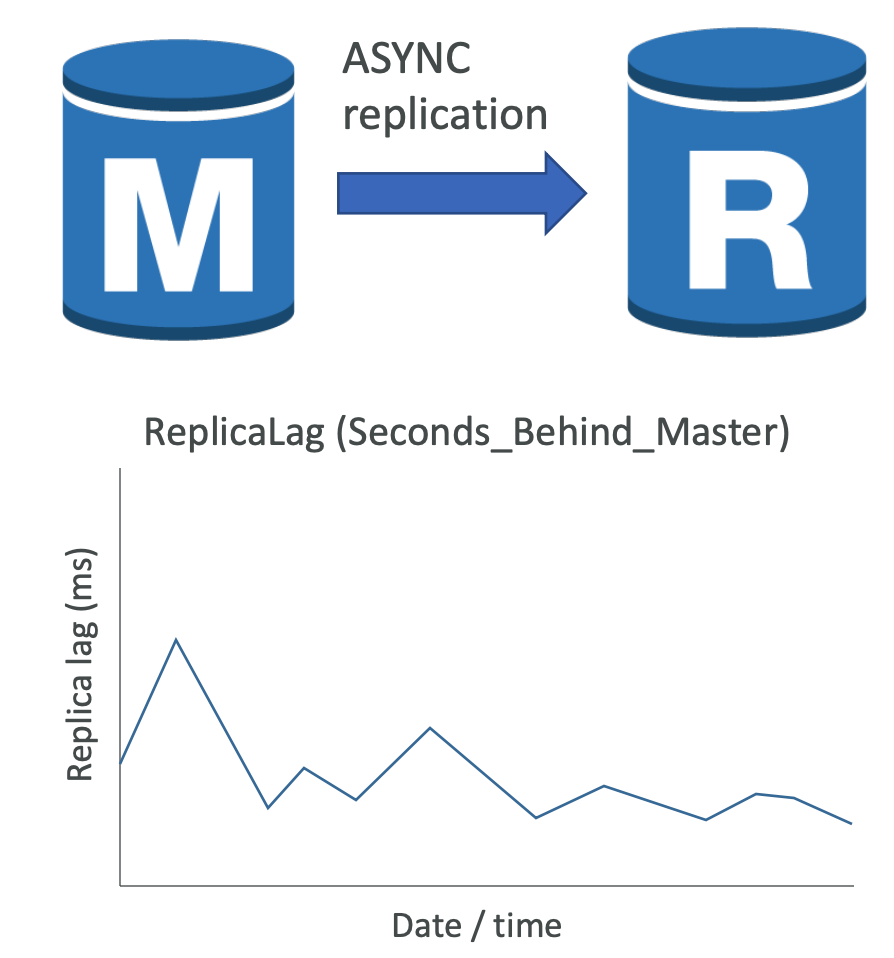
- Asynchronous logical replication typically results in replica lag
- You can monitor ReplicaLag metrics in CloudWatch
- ReplicaLag metric reports Seconds_Behind_Master values
- Replication deplays can happen due to:
- Long-running queries on the primary instance (slow query log can help)
- Insufficient instance class size or storage
- Parallel queries executed on the primary instance
Troubleshooting replication errors
Recommendations:
- Size the replica to match the source DB (storage size and DB instance class)
- Use compatible DB parameter group settings for source DB and replica
- Ex.max_allowed_packet for read replica must same as that of the source DB instance
- Monitor the Replication State field of the replica instance
- If Replication State = Error, then see error details in the Replication Error field
- Use RDS event notifications to get alerts on such replica issues
- Writing to tables on a read replica
- Set read_only=0 to make read replica writable
- Use only for maintenance tasks (like creating indexes only on replica)
- If you write to tables on read replica, it might make it incompatible with source DB and break the replication
- So set read_only=1 immediately after completing mainetance tasks
- Replication is only supported with transactional storage engines like InnoDB. Using engines like MyISAM will cause replication errors
- Using unsafe nondeterministic queries such as SYSDATE() can b reak replication
- You can either skip replication errors (if its not a major one) or delete and recreate the replica
Troubleshooting MySQL read replica issues
- Errors or data inconsistencies b/w source instance and replica
- Can happen due to binlog events or InnoDB redo logs aren't flushed during a replica or source instance failure
- Must manually delete and recreate the replica
- Preventive recommendations:
- sync_binlog=1
- innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1
- innodb_support_xa=1
- These settings might reduce performance (so test before moving to production)
Performance hit on new read replicas
- RDS snapshots are EBS snapshots stored in S3
- When you spin up a new replica, its EBS volume loads lazily in the background
- This results in first-touch penalty (when you query any data, it takes longer to retrieve it for the first time)
- Suggestions:
- If DB is small, run "SELECT * FROM <table>" query on each table on the replica
- Initiate a full table scan with VACUUM ANALYZE (in PostgreSQL)
- Another reason could be an empty buffer pool (cache for table and index data)
Scaling in RDS
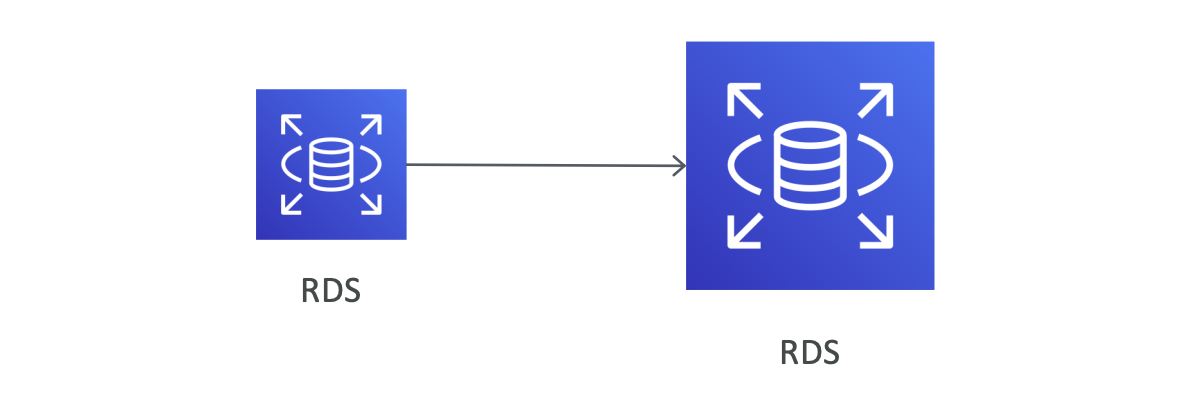
- Vertical Scaling (Scaling up)
- Single-AZ instance will be unavailable during scaling op
- Multi-AZ setup offers minimal downtime during scaling op-standby DB gets upgraded first and then primary will failover to the upgraded instance
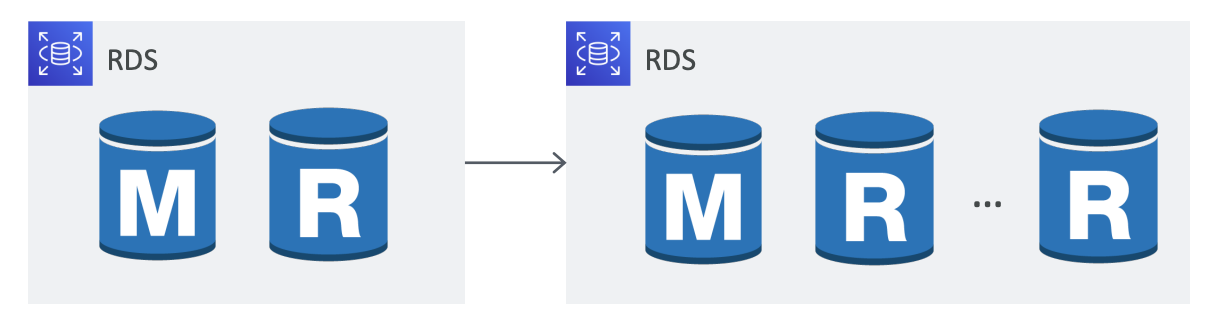
- Horizontal Scaling (Scaling out)
- Useful for read-heavy workloads
- Use read-replicas
- Replicas also act as a DR target
Sharding in RDS
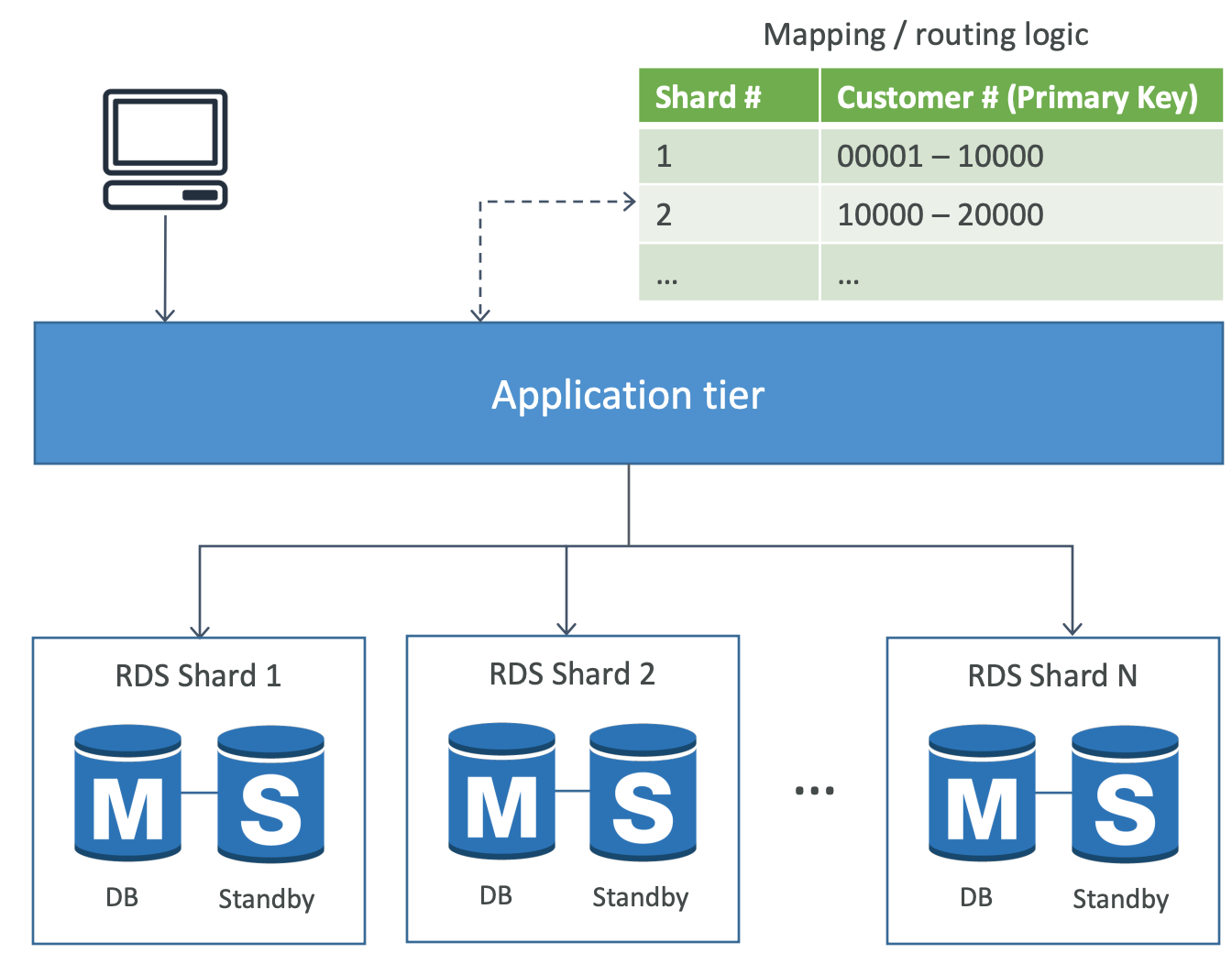
- Sharding = horizontal partitioning
- Split and distribute data across multiple DBs (called shards)
- Mapping / routing logic maintained at application tier
- Offers additional fault tolerance (since no single point of failure)
- If any shard goes through failover, other shards are not impacted
'AWS Database > AWS RDS & Aurora' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AWS Certificate]-Amazon Aurora (0) | 2022.01.06 |
|---|---|
| [AWS Certificate]-Amazon RDS Good thing to know (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [AWS Certificate]-Amazon RDS Monitoring and Logs (0) | 2022.01.06 |
| [AWS Certificate]-Amazon RDS Backup & Restore (0) | 2022.01.05 |
| AWS RDS Aurora 스토리지 및 IO 비용 계산 (0) | 2021.12.20 |

